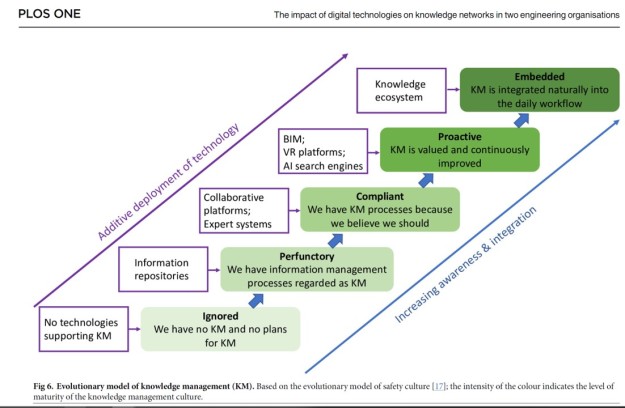
Towards the end of last year, I wrote about the challenges in deploying digital technologies in holistic approaches to knowledge management in order to gain organizational value and competitive advantage [see ‘Opportunities lost in knowledge management using digital technology’ on October 25th, 2023]. Almost on the last working day of 2023, we had an article published in PLOS ONE (my first in the journal) in which we explored ‘The impact of digital technologies on knowledge networks in two engineering organizations’. We used social network analysis and semi-structured interviews to investigate the culture around knowledge management, and the deployment of digital technologies in support of it, in an engineering consultancy and an electricity generator. The two organizations had different cultures and levels of deployment of digital technologies. We proposed a new evolutionary model of the culture of knowledge management based on Hudson’s evolutional model of safety culture that is widely used in industry. Our new model is illustrated in the figure from our article, starting from ‘Ignored: we have no knowledge management and no plans for knowledge management’ through to ‘Embedded: knowledge management is integrated naturally into the daily workflow’. We also proposed that social networks could be used as an indicator of the stage of evolution of knowledge management with low network density and dispersed networks representing higher stages of evolution, based on our findings for the two engineering organizations.
Hudson, P.T.W., 2001. Safety management and safety culture: the long, hard and winding road. Occupational health and safety management systems, pp.3-32, 2001
Patterson EA, Taylor RJ, Yao Y. The impact of digital technologies on knowledge networks in two engineering organisations. PLoS ONE 18(12): e0295250, 2023.